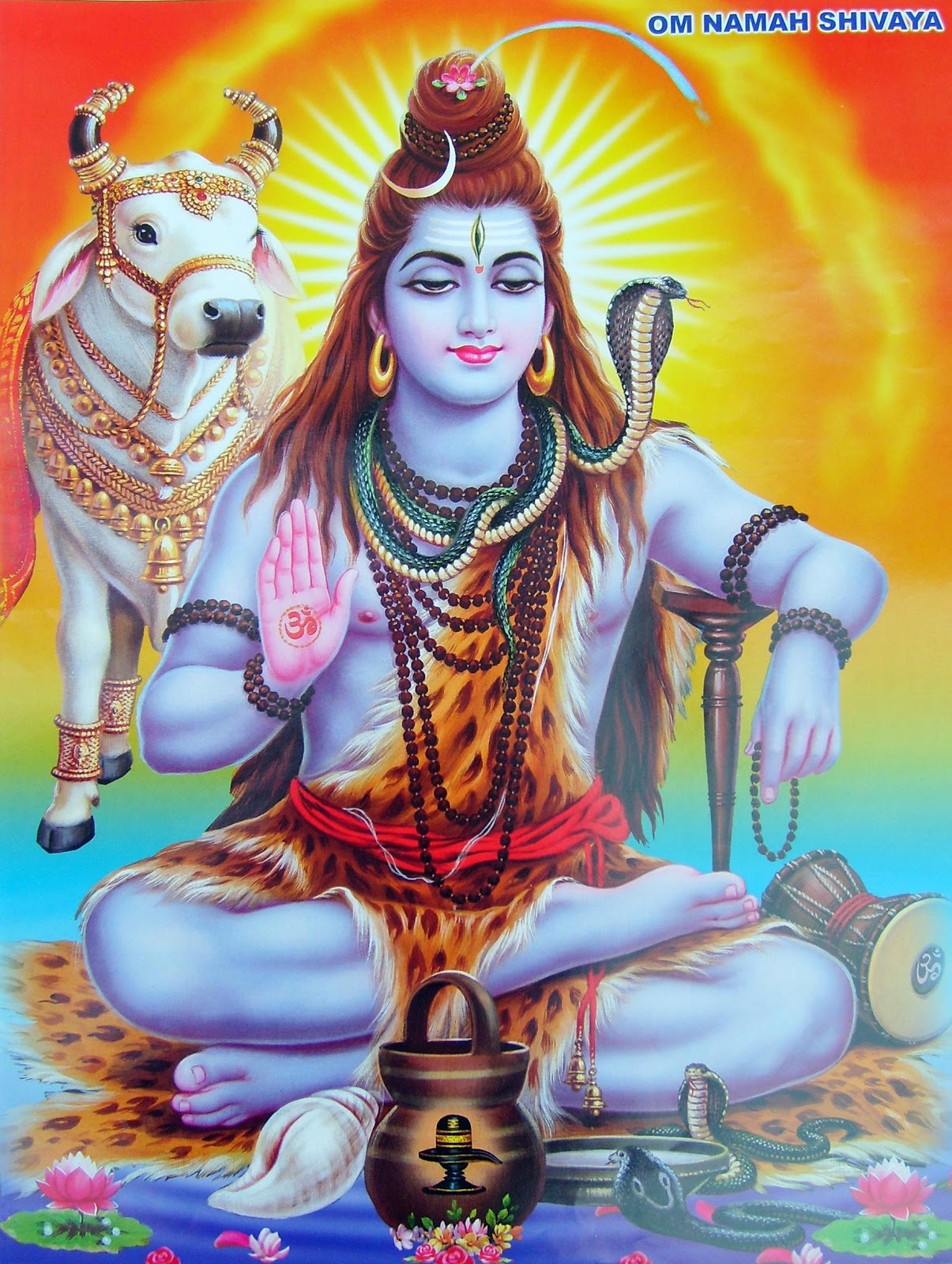
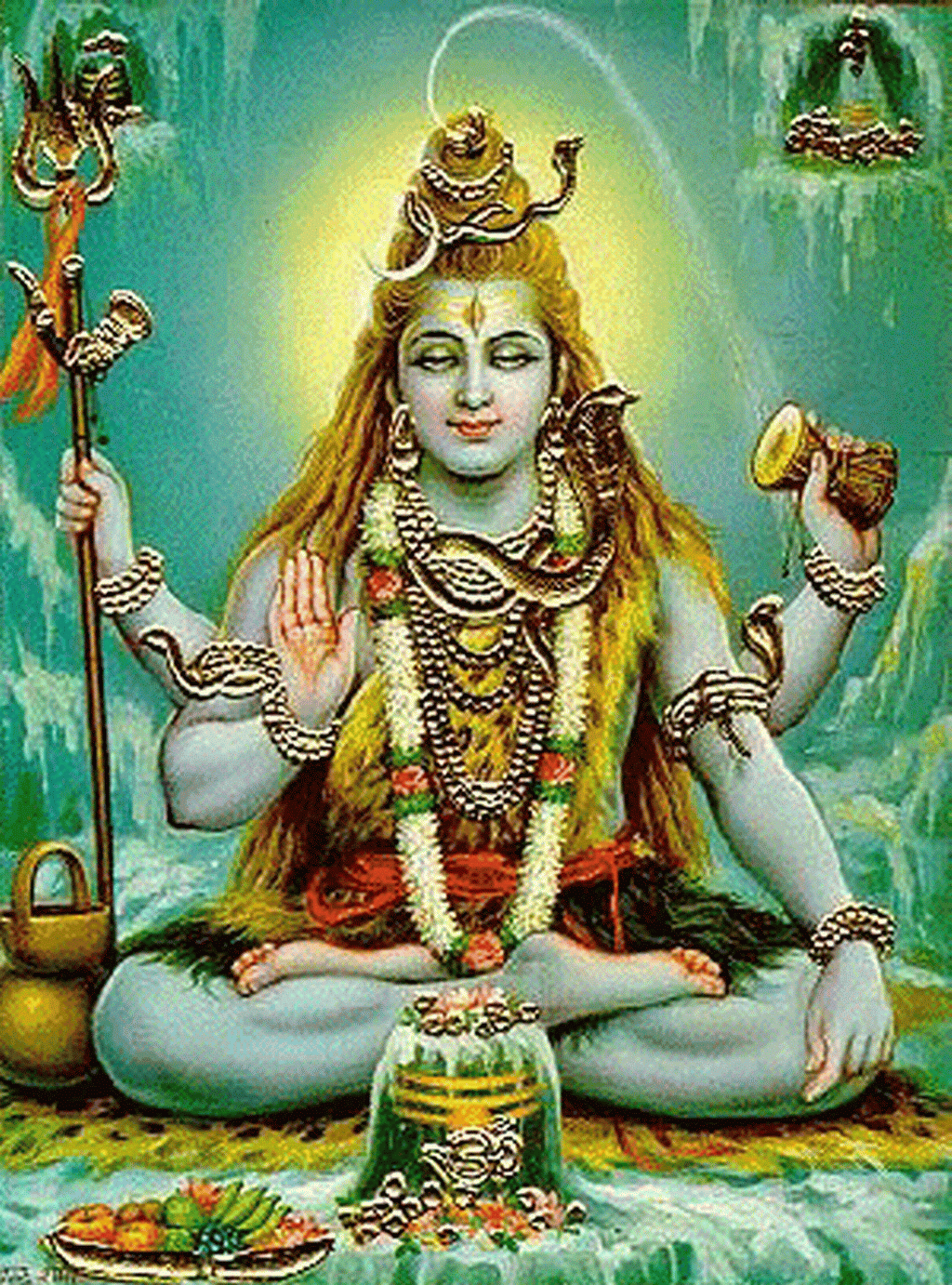
Shiva God, known as the Destroyer in the Holy Trinity of Hinduism, embodies the duality of creation and destruction, love and fear, and asceticism and sensuality. Revered by millions as a divine figure, Shiva is often depicted with distinctive attributes that symbolize his power and mystique. His third eye, serpents, and the crescent moon on his head are not just embellishments; they signify profound philosophical concepts that resonate with his followers. This article delves into the fascinating world of Shiva God, exploring his significance, attributes, and the multitude of ways he is worshipped across various cultures.
In the vast tapestry of Hindu mythology, Shiva God stands out not only as a deity but also as a complex character who transcends the conventional boundaries of divinity. He is both the creator and the destroyer, embodying the cyclical nature of existence. Devotees often seek his blessings for transformation, renewal, and liberation from worldly attachments. This article aims to answer questions about the essence of Shiva God, his role in Hinduism, and the rituals that honor him.
As we journey through the life and teachings of Shiva God, we will uncover his rich mythology, philosophical significance, and the various forms of worship that have evolved over centuries. Whether you are a seasoned practitioner or a curious seeker, understanding Shiva is a path to deeper spiritual insights. Join us as we explore the enigmatic world of Shiva God and the profound lessons he offers to humanity.
Who is Shiva God in Hindu Mythology?
Shiva God is one of the principal deities of Hinduism, worshipped as part of the Trimurti, which includes Brahma (the creator) and Vishnu (the preserver). Often referred to as Mahadeva or the Great God, Shiva embodies a complex interplay of opposing forces. He represents both the ascetic and the householder, the yogi who renounces worldly pleasures, and the God who enjoys the company of his consort, Parvati.
What Are the Key Attributes of Shiva God?
The attributes of Shiva God are rich with symbolism and meaning. Here are some key features that define his persona:
- Third Eye: Represents wisdom, perception, and the ability to see beyond the ordinary.
- Crescent Moon: Symbolizes the passage of time and the cyclical nature of life.
- Trident (Trishula): Represents the three aspects of existence: creation, preservation, and destruction.
- Serpents: Signify power and the ability to overcome fear.
- Damaru (Drum): Represents the cosmic sound of creation, vibrating through the universe.
What Is the Significance of Shiva God in Hindu Worship?
Shiva God holds immense significance in Hindu worship and spirituality. He is revered as a source of strength and transformation, often invoked during rituals for personal and communal well-being. His worship involves various practices, including chanting mantras, performing rituals, and participating in festivals such as Maha Shivaratri, which celebrates his divine energy and grace.
What Are Some Popular Myths and Stories Related to Shiva God?
The mythology surrounding Shiva God is rich and varied, with numerous stories that illustrate his powers and virtues. One of the most famous tales is the story of the churning of the ocean (Samudra Manthan), where Shiva consumes the poison that emerges from the ocean to protect the universe. This act of self-sacrifice highlights his role as the protector and sustainer of life.
How Do Devotees Celebrate Shiva God?
Devotees celebrate Shiva God in various ways, expressing their devotion through rituals and festivals. Some common practices include:
- Offering Water and Milk: Devotees pour water or milk over Shiva Lingams as a symbol of purification and devotion.
- Chanting Mantras: Reciting powerful mantras like "Om Namah Shivaya" to invoke Shiva's blessings.
- Participating in Maha Shivaratri: Observing a night of fasting and prayer dedicated to Shiva.
- Visiting Temples: Pilgrimage to sacred sites like Kashi, Kedarnath, and Amarnath.
What Lessons Can We Learn from Shiva God?
Shiva God teaches valuable lessons that transcend religious boundaries. Some of the key teachings include:
- Embrace Change: Life is a cycle of creation and destruction; embracing change is essential for growth.
- Self-Realization: The journey inward is as important as the journey outward.
- Balance: Finding harmony between opposing forces—work and rest, materialism and spirituality—is vital for holistic living.
What Is the Biography of Shiva God?
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Name: | Shiva |
| Consort: | Parvati |
| Children: | Ganesha, Kartikeya |
| Mantra: | Om Namah Shivaya |
| Symbol: | Shiva Lingam |
| Significance: | Transformation, destruction, and regeneration |
What Are the Different Forms and Avatars of Shiva God?
Shiva God is worshipped in various forms and avatars, each representing different aspects of his divine nature. Some notable forms include:
- Nataraja: The Lord of Dance, symbolizing the cosmic cycles of creation and destruction.
- Bhairava: A fierce aspect representing the annihilation of ego and ignorance.
- Ardhanarishvara: A composite form of Shiva and Parvati, symbolizing the unity of masculine and feminine energies.
Conclusion: Embracing the Wisdom of Shiva God
Shiva God is a multifaceted deity whose teachings resonate across cultures and generations. His life and attributes serve as a reminder of the transformative power of faith, the importance of balance, and the acceptance of change. Whether through rituals, stories, or deep philosophical insights, Shiva God invites us to embark on a journey of self-discovery and spiritual awakening. Embrace his wisdom, and let the essence of Shiva guide you towards a path of enlightenment and inner peace.
Article Recommendations
- Meet Steve Carells Dad A Look At His Life
- Megan Foxs Surprising Talents That You Might Not Know About
- Senate Leader Mitch Mcconnell Discharged Update