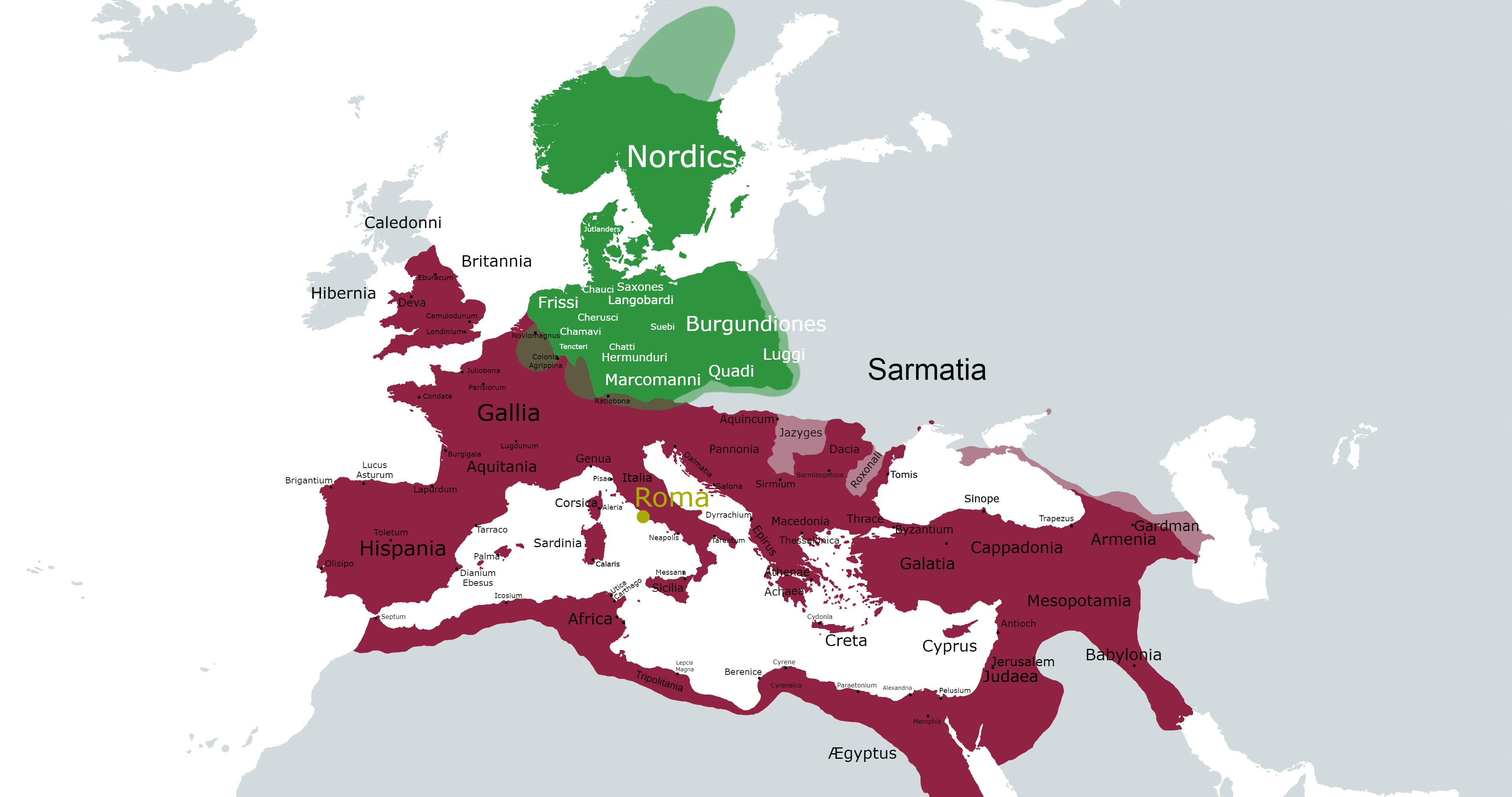
The Eastern Germanic tribes have long fascinated historians and linguists alike, as they represent a unique branch of the larger Germanic family. These tribes, known for their distinctive languages and cultures, have played a crucial role in shaping the history of Europe. From the early migrations to their interactions with neighboring cultures, the Eastern Germanic peoples have left an indelible mark on the historical landscape. As we delve into the world of Eastern Germanic, we uncover not just their linguistic contributions but also their societal structures, beliefs, and the challenges they faced throughout history. This article aims to illuminate the often-overlooked aspects of Eastern Germanic civilization.
The Eastern Germanic tribes, which include the Goths, Vandals, and Burgundians, were instrumental in the transition from antiquity to the Middle Ages. They ventured far beyond their original homelands in Scandinavia and northern Europe, establishing kingdoms and influencing the cultures they encountered. Their legacy continues to resonate in modern times, with echoes of their language and traditions still present in various European cultures.
In this exploration of Eastern Germanic history, we will address key questions about their origins, migrations, and cultural significance. By examining the evidence left behind in artifacts, language, and historical texts, we aim to paint a comprehensive picture of these remarkable tribes and their enduring influence on European history.
What Were the Origins of Eastern Germanic Tribes?
The origins of the Eastern Germanic tribes can be traced back to the early Germanic migrations around the first century AD. They emerged as distinct groups as they moved southward from Scandinavia into what is now modern-day Germany and beyond. The Goths, for example, are believed to have split into two main branches: the Visigoths and Ostrogoths. This division would later play a significant role in their interactions with the Roman Empire and other cultures.
How Did the Eastern Germanic Tribes Migrate?
The migrations of the Eastern Germanic tribes were driven by a variety of factors, including climate change, population pressures, and the quest for resources. These tribes often moved in search of fertile lands and better living conditions. The Goths and Vandals, for instance, famously migrated across Europe, clashing with the Roman Empire and eventually establishing their own kingdoms in regions such as Spain and North Africa.
What Cultural Contributions Did Eastern Germanic Tribes Make?
Eastern Germanic tribes contributed significantly to the cultural landscape of Europe. Their languages, such as Gothic and Vandalic, are part of the Germanic language family and have influenced modern languages. Additionally, their art, craftsmanship, and societal structures showcased a blend of their indigenous traditions and the influences of the cultures they encountered. The Gothic architecture that emerged later in Europe can trace its roots back to the artistic expressions of these tribes.
Who Were the Key Figures in Eastern Germanic History?
Several key figures emerged from the Eastern Germanic tribes, each contributing to their legacy. Notable leaders include:
- Alaric I: The first king of the Visigoths, known for his sack of Rome in 410 AD.
- Theodoric the Great: King of the Ostrogoths who ruled over Italy and promoted a blend of Roman and Gothic cultures.
- Genseric: The king of the Vandals, famous for his naval prowess and the establishment of a powerful Vandal kingdom in North Africa.
What Was the Role of Religion Among Eastern Germanic Tribes?
Religion played a significant role in the lives of Eastern Germanic tribes. Initially, they practiced polytheistic beliefs, worshiping gods and goddesses linked to nature and war. However, with the expansion of Christianity across Europe, many tribes began to adopt the new faith. The conversion of the Goths to Arian Christianity was particularly notable, as it marked a significant cultural shift within the tribe.
How Did Eastern Germanic Tribes Influence Modern Europe?
The influence of Eastern Germanic tribes can still be felt today. Their languages have left a lasting impact on European linguistics, and their historical narratives are woven into the fabric of many modern nations. The migration patterns of these tribes contributed to the formation of several European countries, and their interactions with the Roman Empire helped shape the political landscape of ancient Europe.
What Challenges Did the Eastern Germanic Tribes Face?
Despite their significant contributions, Eastern Germanic tribes faced numerous challenges throughout their history. From conflicts with the Roman Empire to internal divisions, the path was fraught with difficulties. The decline of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century also led to increased competition among tribes for power and resources.
What Legacy Do Eastern Germanic Tribes Leave Behind?
The legacy of Eastern Germanic tribes is one of resilience and adaptability. Their ability to forge new identities in the face of adversity has left a lasting imprint on European culture and history. Through their migrations, conquests, and interactions with other civilizations, they laid the groundwork for the complex tapestry of modern Europe.
Conclusion: Why Study Eastern Germanic History?
Studying the history of Eastern Germanic tribes provides valuable insights into the development of European civilization. Their contributions to language, culture, and societal structures continue to be relevant today. By understanding their past, we can better appreciate the rich tapestry of history that has shaped our modern world.
Article Recommendations
- Janice Combs An Iconic Influence In Entertainment And Fashion
- Mitch Mcconnell Mueller Legislation Senate Impact
- The Amazing Spiderman Cast Stars Roles