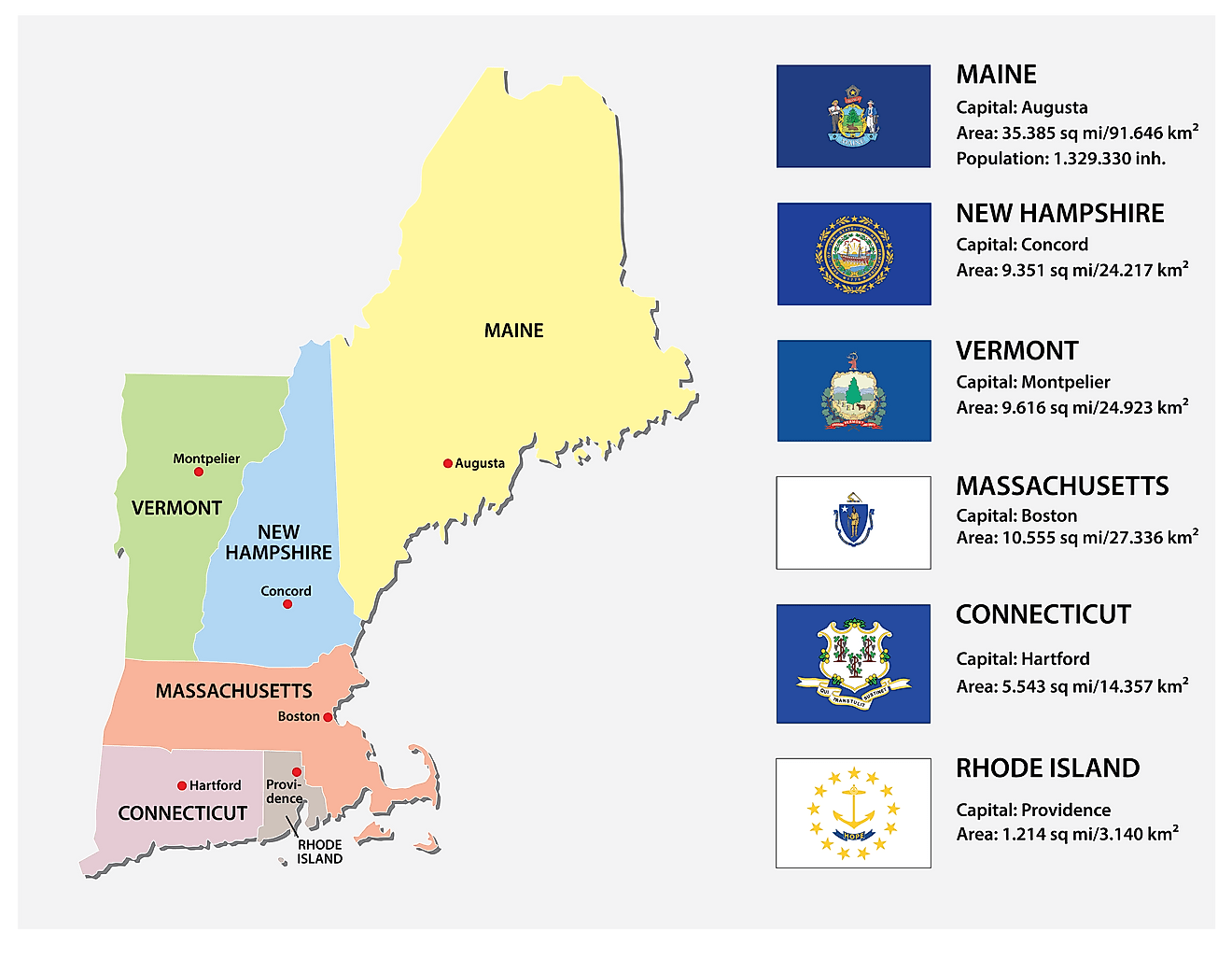
The New England region of the United States is known for its rich history, charming landscapes, and vibrant culture. However, one intriguing aspect that often draws curiosity is the relatively small size of its individual states. Comprising six states—Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut—New England stands in stark contrast to many larger regions across the country. This peculiarity invites a closer look at the historical, geographical, and political factors that contribute to the compactness of this region.
At first glance, the smallness of New England's states may seem trivial, but it carries significant implications for identity, governance, and the dynamics of local communities. As we explore the question of "why are the New England states so small," we will delve into the historical context that shaped their borders and the impact this has had on the people who call these states home. From colonial times to modern-day politics, the evolution of New England's geography tells a story of adaptation and survival.
In this article, we will uncover the historical events, geographical features, and socio-political factors that have contributed to the unique characteristics of New England states. By examining the intricate tapestry woven by history, we aim to answer the question: why are the New England states so small? Join us as we explore this fascinating topic.
What Historical Events Led to the Formation of New England's Borders?
The origins of New England's small states can be traced back to the colonial era. During the 17th century, English settlers arrived on the shores of North America, establishing colonies that would eventually form the backbone of the New England region. The early settlers faced numerous challenges, including harsh winters and conflicts with Indigenous peoples, which influenced their settlement patterns.
As these colonies expanded, they were often created based on geographical features such as rivers and mountains, which naturally delineated boundaries. This led to the establishment of smaller regions that would eventually become the states we know today. The intricate negotiations between settlers and Indigenous tribes, as well as the shifting allegiances among colonial powers, further shaped the borders of New England states.
How Did Geography Influence the Size of New England States?
Geographically, New England is characterized by a diverse landscape, including mountains, forests, rivers, and a rugged coastline. These features played a crucial role in determining the size and shape of the states. For instance, the Appalachian Mountains serve as a natural barrier that influenced settlement patterns, leading to the establishment of smaller states nestled within the valleys and hills.
The region's proximity to the Atlantic Ocean also contributed to its unique geography. Coastal access facilitated trade and communication, prompting the growth of port towns and cities. However, this accessibility also meant that states had to compete for resources and influence, resulting in a tendency to create smaller political entities to better manage local affairs.
What Role Did Statehood Play in Shaping New England's Size?
When it came time for the New England colonies to declare statehood, the desire for local governance and representation played a significant role in shaping their sizes. The early leaders recognized the importance of having a government that could respond quickly to the needs of its citizens, which often favored smaller, more manageable political units.
This inclination toward smaller states was further reinforced during the drafting of the U.S. Constitution. The framers sought to balance the interests of both large and small states, leading to compromises that facilitated the admission of smaller states into the Union. As a result, New England's states became emblematic of a broader trend toward localized governance, shaping their compact nature.
Why Are the New England States So Small Compared to Others?
When comparing New England states to those in other regions, it becomes evident that size is not the only factor influencing governance and identity. In contrast to larger states like Texas and California, New England's compactness fosters a sense of community and local pride. The smallness of these states allows for closer connections among residents, facilitating grassroots movements and community engagement.
Moreover, the historical context of New England's development reflects a unique blend of influences that differ from those found in larger states. The focus on local governance, combined with the region's rich cultural heritage, has contributed to the distinct character of each state. This raises the question: how do these factors impact the daily lives of residents in New England?
What Are the Cultural Impacts of Small State Size in New England?
The small size of New England states has profound implications for their cultural identity. With tight-knit communities and a shared history, residents often take pride in their local traditions, festivals, and customs. This sense of belonging fosters a unique cultural landscape that is distinctly New England.
Furthermore, the small size allows for greater accessibility to local government and civic engagement. Residents can more easily participate in town meetings, voice their opinions, and influence policy decisions. This active involvement in governance contributes to a culture of civic responsibility and engagement that is often less pronounced in larger states.
How Does Small State Size Affect Political Representation?
Political representation in New England is also shaped by the small size of its states. With smaller populations and districts, residents often have more direct access to their elected officials. This fosters a sense of accountability and responsiveness in government, as politicians are more likely to be aware of local issues and concerns.
This close-knit political environment encourages collaborative decision-making and community involvement, allowing residents to actively shape the direction of their states. As a result, New England has a tradition of progressive policies and innovative governance that reflects the values of its residents.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Small State Size?
Like any region, New England's small states come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages. Some potential benefits include:
- Community Engagement: Smaller states foster close-knit communities where residents are more likely to engage with local governance and participate in civic activities.
- Accessibility: Residents often have easier access to politicians and government officials, allowing for greater representation and accountability.
- Unique Cultural Identity: The compact nature of the states contributes to a rich tapestry of local traditions, festivals, and customs.
However, there are also challenges associated with small state size:
- Limited Resources: Smaller states may face challenges in terms of funding and resources, which can impact public services and infrastructure.
- Political Influence: Smaller populations may result in a reduced political influence on the national stage, making it more challenging to advocate for state interests.
- Economies of Scale: Smaller states may struggle to achieve economies of scale in certain industries, potentially impacting economic growth.
How Do New England States Compare to Other Regions?
When examining the size of New England states in comparison to other regions in the United States, it becomes clear that this compactness is a defining characteristic. While states in the Midwest and the South often boast larger land areas and populations, New England's states prioritize local governance and community engagement.
This difference in approach reflects the historical and cultural context of the region, where a strong emphasis on local identity and close-knit communities has shaped political structures. The contrast serves as a reminder of the diverse ways in which states can be organized and governed, each reflecting the unique needs and values of their residents.
What Lies Ahead for New England's Small States?
As New England continues to evolve, the question of "why are the New England states so small" remains relevant. The region faces challenges related to economic growth, demographic changes, and shifting political landscapes. However, the compact nature of these states provides opportunities for innovation, collaboration, and community engagement.
Looking ahead, it will be essential for residents and leaders to navigate these challenges while preserving the unique cultural identity that defines New England. By embracing their small size and fostering a spirit of collaboration, New England's states can continue to thrive in the face of change.
In conclusion, the small size of the New England states is a fascinating topic that encompasses a rich history, unique geography, and vibrant culture. By understanding the intricate factors that have shaped these states, we can appreciate the challenges and advantages that come with being part of this remarkable region. Ultimately, the story of New England is one of resilience, adaptability, and a deep-rooted sense of community.
Article Recommendations
- Shani Darden Expert Tips Advice
- Uncover The Enchanting World Of Dawn Harper Insights From Aubrey K Millers Performance
- Mitch Mcconnell As A Drag Queen An Unexpected Transformation